How To Pick Undervalued Stocks For Investment
Investing in stocks offers an opportunity for significant financial growth, but it also comes with risks. One approach that investors often use is to find undervalued stocks, those that are trading for less than their intrinsic value. Identifying these stocks can give investors a chance to buy shares at a lower price before they eventually rise to their true value. But how do you go about picking undervalued stocks? In this article, we'll break down the key strategies and metrics that investors can use to find undervalued stocks for investment in 2025.
What Are Undervalued Stocks
Before diving into the methods to pick undervalued stocks, it's important to understand what makes a stock undervalued. Essentially, an undervalued stock is selling for less than its true worth, which is often calculated through fundamental analysis. When a stock is undervalued, it may be overlooked or mispriced by the market, creating an opportunity for savvy investors to purchase it at a bargain price.

Market inefficiencies, short-term volatility, and external factors such as market sentiment can all contribute to undervaluation. However, it’s important to note that not all undervalued stocks are good investments. The underlying reason for the undervaluation must be understood, as it could be due to negative factors that could further depress the stock’s price in the future.
Key Metrics To Look For
To identify undervalued stocks, investors need to focus on key financial metrics. These metrics help assess a company’s performance, growth potential, and the price at which the stock is trading relative to its true value. Below are some of the most important metrics to consider when evaluating a stock’s value.
Price-To-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)
One of the most commonly used metrics to assess whether a stock is undervalued is the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio. This ratio compares the stock price to the company’s earnings per share (EPS), giving investors a quick snapshot of how much they are paying for each dollar of earnings. A lower P/E ratio could indicate that the stock is undervalued, especially when compared to industry peers or the market as a whole.
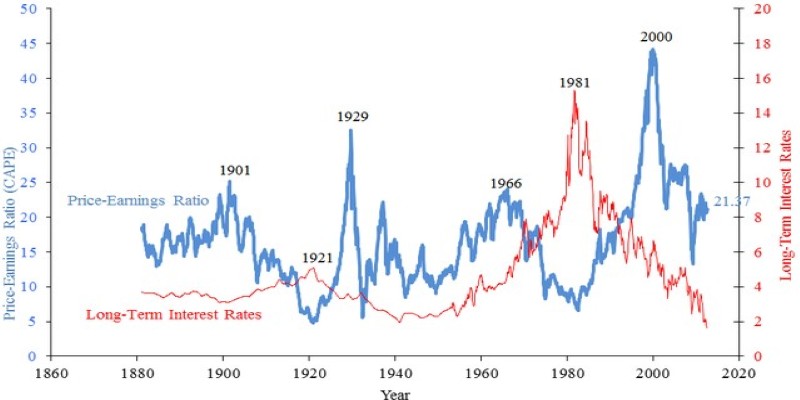
However, a low P/E ratio can also signal that the company is facing challenges, so it's crucial to analyze the context in which the ratio is low. For example, if a company is in a cyclical industry or undergoing temporary setbacks, the stock might be undervalued despite a low P/E ratio.
Price-To-Book Ratio (P/B Ratio)
The price-to-book (P/B) ratio compares a company's market value to its book value. A P/B ratio under 1.0 can suggest that a stock is undervalued, as it means the market is valuing the company's shares for less than the company's actual assets. However, just like the P/E ratio, the P/B ratio should be evaluated with caution. Companies with low P/B ratios might be facing significant risks, or they may be in industries where assets do not represent the true value of the business, such as technology companies, where intellectual property and brand recognition are more valuable than physical assets.
Dividend Yield
Another metric that can point to undervalued stocks is the dividend yield. A high dividend yield may indicate that a stock is undervalued if the company continues to pay out a consistent or growing dividend. Investors often see high yields as an attractive feature, especially in a market where growth stocks may not offer immediate returns.
However, a high dividend yield can also be a red flag, signalling that the stock price has dropped significantly, making the dividend yield appear high. It's important to assess whether the company's dividend is sustainable and whether its fundamentals support continued dividend payments.
Risk Factors And Red Flags
Investing in undervalued stocks can be rewarding, but it also comes with risks. Before buying any stock, it’s essential to assess potential risks that could affect the company's future performance. While market inefficiencies often lead to undervaluation, investors should be aware of situations where the undervaluation may be a reflection of fundamental problems.
Debt Levels
A high level of debt can be a significant risk, especially for companies in industries with unpredictable cash flows. Undervalued stocks with high debt levels may offer potential for growth, but they also carry a higher level of risk. Assess the company’s ability to service its debt, as well as its debt-to-equity ratio, to determine whether the stock is undervalued due to temporary financial struggles or deeper issues.

Legal And Regulatory Risks
Legal and regulatory risks can have a significant impact on a company’s stock price. Companies that are embroiled in legal battles or face regulatory scrutiny may experience volatility in their stock price. While these risks may sometimes cause undervaluation, it’s essential to assess the potential impact of such issues before investing. Ensure that the company’s legal and regulatory challenges are not severe enough to affect its long-term prospects.
Economic And Market Conditions
Overall economic conditions can also influence whether a stock is undervalued. Economic downturns, rising interest rates, or geopolitical instability can all create market conditions that lead to undervaluation. While these factors may present buying opportunities, they can also signal that the company’s challenges are likely to persist in the near future. It’s crucial to assess whether the stock’s undervaluation is due to broader market conditions or specific issues tied to the company itself.
When To Buy And Sell
Once you've identified undervalued stocks, it’s important to determine the best time to buy and sell. Patience is often key when investing in undervalued stocks, as it may take time for the market to recognize their true value. However, investors should also know when to sell. If the stock has appreciated to a point where it is no longer undervalued or if the company’s fundamentals change for the worse, it may be time to exit the position.

Conclusion
Picking undervalued stocks requires a combination of quantitative analysis and qualitative evaluation. While financial metrics such as P/E ratio, P/B ratio, and dividend yield are essential for identifying undervalued stocks, it's also crucial to assess the company’s management, competitive advantage, and market conditions. Moreover, risk factors such as debt levels and legal issues should not be overlooked.
With the right research and strategy, investing in undervalued stocks can be a rewarding way to build wealth over time. Remember, the key to successful investing lies in thorough analysis, patience, and a keen understanding of both the financial and qualitative aspects of the companies you invest in.





